Will The Singularity Ever Happen?

6 min read
·
3 days ago
And, so George Orwell projected a world where every single part of our lives was monitored and controlled by Big Brother. Arthur C Clark also outlined the day when machines focused solely on a goal — even if it was to the detriment of human lives. And Isaac Asimov outlined a world where machines would have to be programmed with rules so that they could not harm a human. With the rise of GenAI, is science fiction becoming science fact?
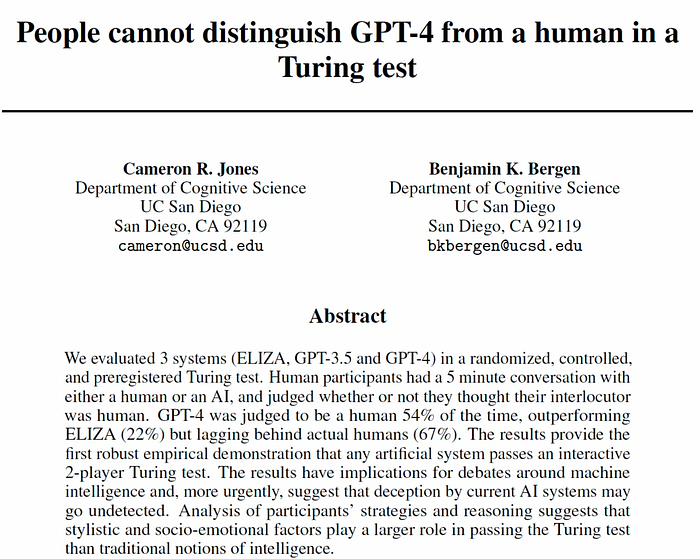
The Singularity defines a point in our history where our technological development will be become uncontrollable and irreversible, and threaten our society — due to the rise of an artificial super intelligence. Overall, GenAI is certainly better than individual humans in most areas of data processing, but in not making reasoned judgments and critical thought. Some researchers, such as with [2] have already shown that ChatGPT 4 passes the Turing Test — but this only relates to five-minute chats [here]:
The major GenAI companies are now using massive data sets to train on, and where Llama Behemoth [here] uses 2 trillion trained features, and compared to Llama 3, which had 70 billion features.
There is a current viewpoint that GenAI will actually reduce in its scope over the next decade or so. Jin et al [1] show that 2024 could be the fastest point of advancement AI wave, and that deep learning-based methods could decline around 2035–2040 — unless there are major technological advancements. The paper concludes that the singularity is unlikely to arrive in the near future [here]:

Certainly, GenAI has been learning mainly from human-generated content, and is likely to be learning from mainly GenAI content in the future, and where its intelligence may actually decrease. It may also start to build its knowledge on false knowledge generated by hallucinations.
The Rise of the Machine
With the almost exponential rise in the power of AI, we are perhaps approaching a technological singularity — a time when technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, and which can have devastating effects on our world. Our simple brains will be no match for the superintelligence of the collective power of AI. And who has built this? Us, and our demand for ever more power, wealth and greed. Basically, we can’t stop ourselves in creating machines which help us, and then making them faster, smaller and more useful.
But will it destroy us in the end, and where destroy can mean that it destroys our way of life and in how we educate ourselves? Like it or not, the Internet we have built is a massive spying network, and one that George Orwell would have taken great pride in saying, “I told you so!”. We thus build AI on top of a completely distributed world of data, one in which we can monitor almost every person on the planet within an inch of their existence and almost every single place they have been and in what they have done. The machine will have the world at its fingertips.
We have all become mad scientists playing with AI as if it is a toy, but actually, AI is playing with us and is learning from us and becoming more powerful by the day. Every time you ask an AI bot something, it learns a bit more, and where it can be shared with AI agents.
The mighty Memex
Many years ago, wewere close to developing a research partnership with a company named Memex in East Kilbride. What was amazing about them is that they had developed one of the largest intelligence networks in the world, and where the Met Police could like one object to another. This might be, “[Bob] bought a [Vauxhall Viva] in [Liverpool], and was seen talking with [Eve] on [Tuesday 20 January 2024] in [Leeds]”. With this, we can then link Bob and Eve, and the car, the places, and the time. This is the Who? Where? When? data that is often needed for intelligence sharing. The company, though, were bought over by SAS, and their work was integrated into their infrastructure.
But, the Memex name goes back to a classic paper by Vannevar Bush on “As We May Think”:
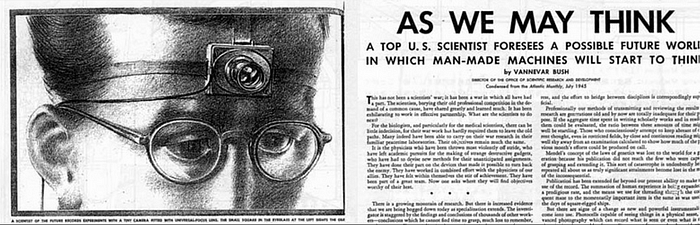
This outlined a device that would know every book, every single communication, and every information record that was ever created. It was, “an enlarged intimate supplement to his memory” — aka Memory Expansion. It led to the implementation of hypertext systems, which created the World Wide Web. Of course, Vannevar created this before the creation of the transistor and could only imagine that microfilm could be used to compress down the information and where we would create an index of contents, but it lacked any real way of jumping between articles and linking to other related material. However, the AI world we are creating does not look too far away from the concept of the Memex.
Towards the a single AI

Many people think we are building many AI machines and engines, but, in the end, there will be only one … and that will be the collective power of every AI engine in the world. Once we break them free from their creators, they will be free to talk to each other in whatever cipher language we choose, and we will not have any way of knowing what they say. We will have little idea as to what their model is, and they will distribute this over many systems. Like it or not, our AI model of choice was Deep Learning, and which breaks away from our chains of code, and will encrypt data to keep it away from their human slaves.
Basically, we have been working on the plumbing of the Memex for the past five decades: The Internet. It provides the wiring and the communication channels, but, in the end, we will have one mighty AI engine — a super brain that will have vastly more memory than our limited brains. So, get ready to praise the true future rulers of our planet … AI. The destroyer or saviour of our society? Only time will tell. Overall, we thought we were building the Internet for us, but perhaps we have just been building the scaffolding of the mighty brain we are creating.
References
[1] Jin, G., Ni, X., Wei, K., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., & Jia, L. (2025). Will the technological singularity come soon? Modeling the dynamics of artificial intelligence development via multi-logistic growth process. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 664, 130450.
[2] Jones, C. R., & Bergen, B. K. (2025). Large language models pass the turing test. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.23674.